SSH IoT Device Through Router: Your Guide To Remote Access And Control
Imagine having your smart devices, sensors, or tiny computers scattered across different locations, perhaps even in your own home, yet feeling completely in charge. You want to check on them, send new commands, or maybe even fix something without physically being there. This desire for remote interaction, especially with an IoT device sitting behind a router, is something many folks, from hobbyists to small business owners, really want to figure out.
The challenge comes when these devices live inside a private network, tucked away behind a router and its firewall. It's a bit like trying to call someone who only accepts calls from within their own house; outside connections just don't get through directly. This setup, while good for security, makes remote management a tricky puzzle, so you might wonder how to get past it.
Luckily, there are ways to bridge this gap, and one of the most trusted methods involves using Secure Shell, or SSH. It's a powerful tool that helps you create a safe channel to your IoT gadget, even if it's hidden behind a router. This guide will show you how to set up and use SSH to connect to your IoT device, offering practical advice and looking at different ways to make that connection happen, too it's almost a complete roadmap.
- Ish Smith 3pt Percentage 2023 24
- Jcpenney East Brunswick Nj Hours
- Tmz
- Kardashian Familys Net Worth
- Pace Morby Net Worth 2024
Table of Contents
- Why Remote SSH for IoT Devices?
- The Router Challenge: NAT and Firewalls
- Traditional Approach: Port Forwarding
- Smarter Ways to Connect Without Direct Port Forwarding
- Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device
- Securing Your SSH Connection
- Practical Uses of Remote SSH
- Troubleshooting Common SSH Issues
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Remote SSH for IoT Devices?
Having remote access to your IoT devices is, you know, incredibly useful for many reasons. Think about a smart home setup, or maybe a network of environmental sensors in a far-off field. You need to keep an eye on them, make sure they are working right, and sometimes, even send them new instructions. SSH gives you a secure way to do all that.
For one thing, it helps with monitoring. You can check sensor readings or device status from anywhere, actually. If you're running a Raspberry Pi for a project, you can log in to see its performance or what data it's collecting. This is key for monitoring, controlling, and debugging these tiny computers, so it's a big deal.
Then there's the debugging part. When something goes wrong with an IoT device, being able to SSH in lets you see error logs, restart services, or change settings without having to physically go to the device. This is especially helpful for devices installed in hard-to-reach spots, or if you're managing many of them. It saves a lot of time and effort, you know.
- Undress Ai Tool
- What Happened To Ahmir Duval King Holland
- Roger Federer Twin Daughters Not His
- How Many Followers Does Piper Rockelle Have On Tiktok
- Ashley Sinclair
Finally, remote control is a huge benefit. You can send commands, update software, or even transfer files securely to and from your IoT device using tools like SFTP and SCP. This makes managing your devices much smoother and safer, basically giving you full control over your embedded Linux device from afar.
The Router Challenge: NAT and Firewalls
Most IoT devices, like your smart thermostat or a home security camera, are sitting behind a router in your local network. This router has a very important job: it acts as a gatekeeper between your internal network and the vast internet outside. This setup is great for security, but it also creates a hurdle for remote access, that's for sure.
The main issue here is something called Network Address Translation, or NAT. Your router gives all the devices inside your home a private, local IP address, like 192.168.1.100. From the internet's point of view, all traffic from your home looks like it's coming from a single public IP address, the one your Internet Service Provider gives you. When an outside connection tries to reach your device, the router doesn't know which internal device it should send the request to, so it usually just blocks it.
Adding to this, routers also have built-in firewalls. These firewalls are like security guards, blocking unwanted incoming connections by default. This protection is really good for keeping bad actors out, but it means you can't just directly SSH into your IoT device from the internet. For example, if you can SSH to your router from your IoT device, but not the other way around, it's a clear sign of this firewall and NAT at play.
So, because IoT devices installed behind a NAT router and firewall cannot be accessed from the internet directly, we need clever ways to get around this. This is where different remote access methods come into play, offering ways to punch through or bypass these network barriers, naturally.
Traditional Approach: Port Forwarding
One of the oldest and most straightforward ways to allow outside access to a device on your local network is through port forwarding. This method essentially tells your router, "Hey, if a connection comes in on a specific port from the internet, send it directly to this particular device on my local network." It's like setting up a special delivery instruction for your router, you know.
To set this up, you usually log into your router's administration page. You'd find a section for "Port Forwarding" or "NAT Settings." There, you'd specify an external port (what the internet sees), an internal port (what your device listens on, usually 22 for SSH), and the internal IP address of your IoT device. Once configured, any SSH connection attempting to reach your public IP address on that external port would then be redirected to your IoT device, so it works like a charm.
This method has been used for years to host game servers, web servers, and, yes, even SSH access to devices. It's a common first thought for many who need remote access, and it's relatively simple to set up if you have control over your router's settings. Just a little configuration, and you're good to go, basically.
Pros and Cons of Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is, in a way, a direct solution, and it's fairly simple to set up for many home users. It gives you direct SSH access to your device, which is convenient for quick checks or commands. If you only have one or two devices and you're comfortable with router settings, it can feel like a good fit, you know.
However, there are some significant downsides. The biggest concern is security. When you open a port on your router and point it to an internal device, you're essentially creating a direct path from the internet to that device. This means your IoT device is now exposed to the entire internet, making it a potential target for malicious activity. If your device's SSH service isn't perfectly secure, or if it has a weak password, it could be compromised, which is a serious worry.
Another issue is that your public IP address might change, especially if you have a dynamic IP address from your internet provider. This means your port forward will stop working until you update it or use a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service. Also, if you need to access multiple devices, you'd have to forward a different port for each, which can get complicated and less secure. So, while it's easy, it's often not the best long-term solution, particularly for small businesses or when dealing with many devices.
Smarter Ways to Connect Without Direct Port Forwarding
Given the security and practical issues with direct port forwarding, many people look for better ways to access their IoT devices remotely. These methods avoid opening direct holes in your firewall, making your setup much safer and often more reliable. They typically involve creating an indirect, secure pathway, you know, rather than a wide-open door.
These alternatives are especially good for IT admins and those managing a fleet of devices, as they offer more scalable and secure solutions. They also work well when your IoT devices are behind a strict firewall, or if you're using mobile networks like Starlink, 3G, 4G LTE, or 5G cellular, where direct incoming connections might be tricky or impossible. So, let's look at some of these smarter approaches, that's for sure.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
A Virtual Private Network, or VPN, is a fantastic way to access your IoT devices securely without direct port forwarding. Think of it like creating a private, encrypted tunnel from your remote computer directly into your home or office network. Once you're connected to the VPN, your remote computer essentially becomes part of that local network, as a matter of fact.
To use a VPN for IoT access, you'd typically set up a VPN server on your router, a dedicated device, or even a Raspberry Pi within your local network. Then, from your remote location, you connect to this VPN server using VPN client software. Once the VPN connection is established, you can then SSH into your IoT device using its local IP address, just as if you were sitting right there in your home. This approach works really well because your remote device is virtually inside the network, basically.
VPNs offer strong encryption and keep your network private. They're a very secure option, but they do require some initial setup and maintenance. You need to configure the VPN server and make sure your router allows the VPN traffic. Still, for a highly secure and flexible remote access solution, VPNs are a top choice, and they're often preferred by those who value strong security, too.
Reverse SSH Tunnels
Reverse SSH tunnels are a really clever way to bypass NAT and firewalls without opening any incoming ports on your router. Instead of you initiating a connection to your IoT device, the IoT device itself initiates an outgoing connection to a public SSH server that you control. This outgoing connection is usually allowed by most firewalls, you know.
Here's how it works: Your IoT device establishes an SSH connection to a publicly accessible server (often a small cloud server you rent). As part of this connection, it tells the public server to create a "reverse tunnel." This tunnel effectively says, "Any connection that comes to a specific port on this public server should be forwarded back through this tunnel to my local SSH port (22) on the IoT device." So, when you want to access your IoT device, you SSH into your public server, and then from there, you connect to the specific port that's been tunneled back to your IoT device, that's how it works.
This method is incredibly powerful because the IoT device "calls out" to establish the connection, meaning no incoming ports need to be opened on your home router. It's a very secure and flexible solution, especially for devices behind strict firewalls or mobile networks. It does require you to have a public SSH server, but these are often inexpensive to set up. It's a technique that many professionals use for secure remote access without port forwarding or firewall pinholing, in fact.
Cloud-Based IoT Platforms and Web SSH
For those looking for an even simpler approach, especially without managing their own servers or complex network setups, cloud-based IoT platforms and Web SSH solutions are a great choice. These services provide a ready-made infrastructure for remote access, making things much easier to handle. They essentially abstract away the networking complexities, so you don't have to worry about them.
Many IoT platforms offer built-in remote access features, often using agents installed on your IoT device that connect to their cloud service. This service then acts as a secure intermediary, allowing you to access your device through a web interface or a dedicated client application. This is how you can access IoT devices remotely with SSH and why some smaller businesses might outgrow direct SSH setups quickly, moving to more managed solutions. These platforms often provide features like monitoring, data collection, and even remote command execution, all through a secure web portal.
Some services also offer "free web SSH access for IoT devices," allowing you to connect directly from a web browser. This means you don't need to install any SSH client software on your computer. Accessing remote IoT devices behind a router on an Android device for free is also a growing need, and many of these platforms offer mobile apps or web interfaces that work well on phones and tablets. This guide will look into the best ways to set up remote SSH for IoT devices that are behind a router, using free tools on Android, which helps make sure you have safe and smooth access, really.
Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device
Before you can even think about connecting to your IoT device remotely, you need to make sure SSH is actually running on it. Most Linux-based IoT devices, like Raspberry Pis or other embedded Linux systems, come with SSH capabilities, but it might not be enabled by default. The exact steps will vary a bit depending on your device's operating system and firmware, but the general idea stays the same, you know.
For a Raspberry Pi, for instance, you can enable SSH through the `raspi-config` tool or by placing an empty file named `ssh` (without any extension) in the boot partition of the SD card. After a reboot, the SSH server should be active. For other Linux devices, you might need to install an SSH server package, usually `openssh-server`, using your package manager (like `apt` on Ubuntu or Debian-based systems). Just a simple command like `sudo apt install openssh-server` often does the trick, that's how it usually works.
Once installed, it's a good idea to ensure the SSH service starts automatically when the device boots up. You can typically check its status with `sudo systemctl status ssh` and enable it with `sudo systemctl enable ssh`. Remember, using SSH, you gain secure command-line access to your device, which is incredibly powerful for management and troubleshooting, too it's almost like being there in person.
Securing Your SSH Connection
Having SSH enabled on your IoT device is great for remote access, but it also opens a door. It's super important to make sure that door is secure. A poorly secured SSH connection is an open invitation for trouble, as a matter of fact. There are several key steps you should take to protect your device.
First and foremost, always use SSH key pairs instead of passwords for authentication. This is a much stronger security measure. You generate a public key and a private key. The public key goes on your IoT device, and you keep the private key secure on your computer. When you try to connect, your computer uses the private key to prove its identity to the device, without ever sending a password over the network. This is especially useful if you need to connect to an SSH proxy server using a specific keypair, not your default one.
Secondly, disable password authentication entirely once you have key-based authentication working. This removes the risk of brute-force attacks where attackers try to guess your password. Also, change the default SSH port (which is 22) to a non-standard, high-numbered port. While this isn't a security measure in itself (it's "security by obscurity"), it does reduce the amount of automated scanning and attack attempts your device will see, just a little.
Finally, disable root login over SSH and use a regular user account with `sudo` privileges instead. This means an attacker can't immediately gain full control of your device even if they manage to log in. Regularly update your device's software and SSH server to patch any known vulnerabilities. Setting up SSH on IoT devices and routers is an essential step for anyone looking to enhance their network security and streamline device management, you know, it's a critical part of the process.
Practical Uses of Remote SSH
Once you've got your SSH connection working, a whole world of possibilities opens up for managing your IoT devices. It's not just about running a few commands; SSH is a versatile tool that helps with many common tasks, basically making remote management a breeze.
One very common use is securely transferring files. You can use tools like `scp` (Secure Copy Protocol) or `sftp` (SSH File Transfer Protocol) to move files to and from your IoT device. Whether you need to upload a new software update, download logs for analysis, or back up configuration files, `scp` and `sftp` do it safely. For example, you can learn how to securely transfer files to and from IoT or any remote device using SFTP and SCP, which is super handy.
Another powerful feature is SSH tunneling, also known as port forwarding (but different from the router-level port forwarding we discussed earlier). This allows you to securely tunnel other network traffic over your SSH connection. For instance, if you have a PostgreSQL database running on your IoT device, you can use SSH tunneling to connect to it securely from your local machine with a tool like pgAdmin III. This creates a secure channel for your database traffic, even if the database itself isn't exposed to the internet, so it's very useful.
You can also automate tasks on your IoT device using SSH. If you're writing a script to automate some command line commands in Python, you can use libraries to execute SSH commands remotely. This means you can trigger updates, collect data, or perform maintenance tasks on a schedule, all from your main computer. This really helps streamline operations, you know, especially for multiple devices.
Troubleshooting Common SSH Issues
Even with everything set up correctly, you might run into a few bumps when trying to SSH into your IoT device. It's pretty common, and often, the fix is simpler than you think. Knowing some typical problems and their solutions can save you a lot of frustration, too it's almost a given that you'll encounter something.
One frequent issue is incorrect IP addresses or network configuration. Double-check that you're using the correct IP address for your IoT device, especially if it's a local IP address within your network. Also, make sure your device is actually connected to the network and has an IP address. Sometimes, a simple network restart on the IoT device or router can clear up connection problems, that's often the case.
Firewall settings, both on your router and on the IoT device itself, can block SSH connections. Ensure that any firewalls on your IoT device (like `ufw` on Ubuntu) are configured to allow incoming connections on the SSH port. If you're using port forwarding on your router, verify that the rules are correctly set up and pointing to the right internal IP and port. If you can ping and SSH to the router from your IoT device, but not the other way around, it's a strong hint that the router's firewall or NAT is the culprit, naturally.
SSH key issues are another common headache. If you're using key-based authentication, make sure your private key has the correct permissions (usually read-only for your user) and that the public key is correctly installed in the `~/.ssh/authorized_keys` file on your IoT device. Incorrect file permissions on the `.ssh` directory or `authorized_keys` file can prevent SSH from working. Sometimes, simply running a command to fix permissions, like `chmod 700 ~/.ssh` and `chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys`, can resolve it. If you've recently changed something, like an Apple ID password which affects SSH keys on your Mac, that could also be the cause, as I've seen before.
Finally, check the SSH server status on your IoT device. The SSH service might not be running or could have crashed. You can often restart it with a command like `sudo systemctl restart sshd` or `sudo service ssh restart`. Looking at the SSH server logs (`/var/log/auth.log` or `journalctl -u ssh`) can give you clues about why connections are failing, so it's a good place to start digging.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I SSH into my IoT device from anywhere in the world?
Yes, you can, but it requires setting up a method that bypasses your router's NAT and firewall, like port forwarding (with security risks), a VPN, or a reverse SSH tunnel. Cloud-based IoT platforms also offer this kind of global access, you know, making it simpler.
Is SSH secure enough for my IoT devices?
SSH itself is a very secure protocol, but its security heavily depends on how you configure it. Using strong SSH key pairs, disabling password authentication, changing the default port, and keeping your software updated are vital steps to ensure a secure connection. Without these precautions, it can be vulnerable, so you need to be careful.
What if my IoT device's IP address changes?
If your IoT device gets a dynamic local IP address from your router, you can configure your router to assign a static IP address to the device based on its MAC address. If your public IP address changes, you'll need to use a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service, or a method like reverse SSH tunnels or cloud platforms that don't rely on your public IP, that's often the solution.
- Xxmx
- Como Quitar Manchas Amarillas De Ropa Bebe
- Misskorinne Twitter
- Gooner Setup
- Is Princess Catherine Pregnant With Her Fourth Child
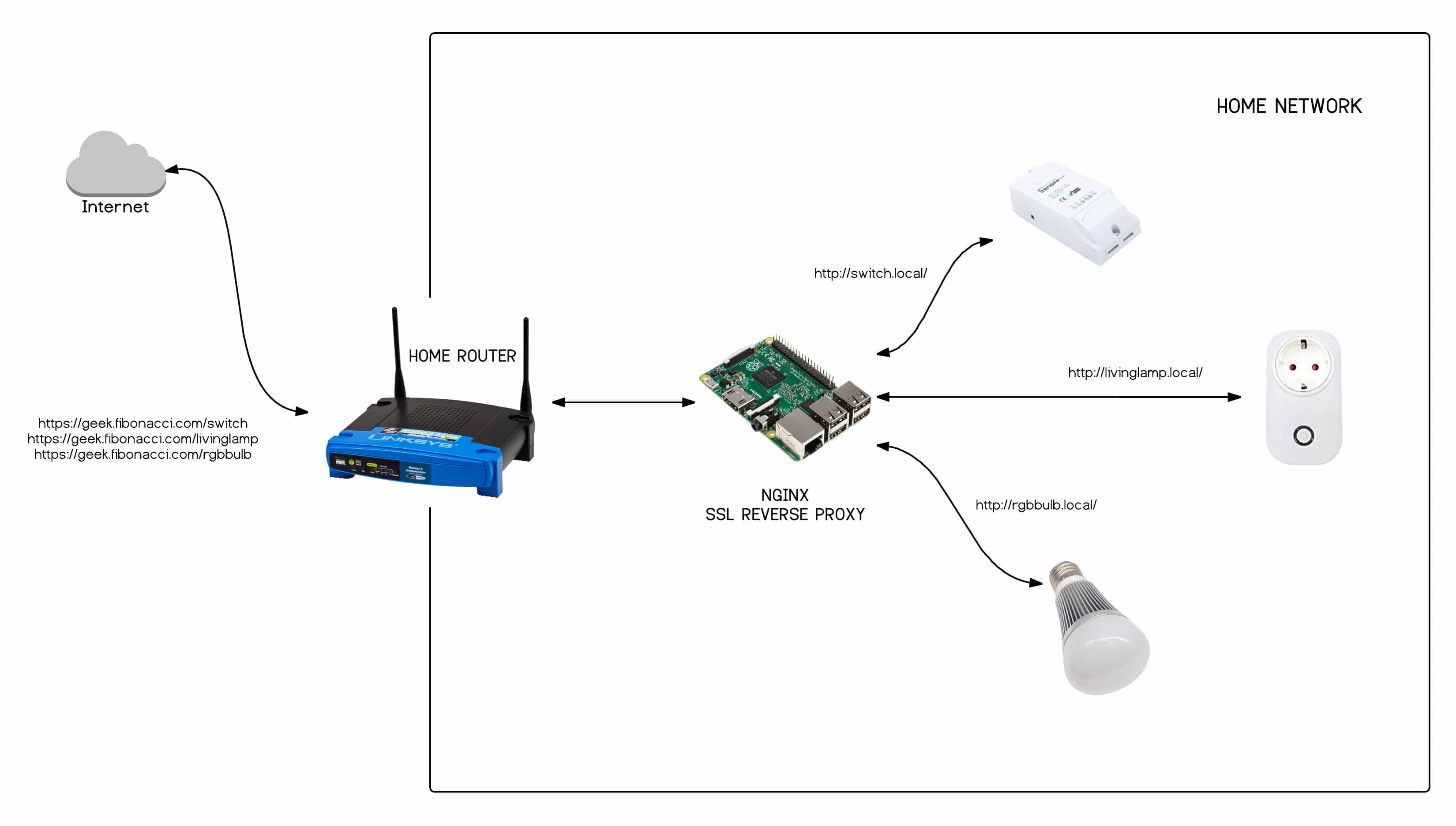
Comprehensive Guide To SSH IoT Device Router Setup
Mastering SSH IoT Device Router Setup: A Comprehensive Guide

SSH into your IoT Enterprise Gateway - NCD.io