Troubleshooting When Your SSH IoT Device Remotely Not Working
It can feel pretty frustrating when you are trying to connect to your Internet of Things (IoT) device from afar, and your usual Secure Shell (SSH) access just isn't happening. You might be accustomed to using tools like PuTTY on a Windows computer or a command line terminal on a macOS system to get into devices like a Network Attached Storage (NAS) without much fuss, but with an IoT gadget, it's a different story. This kind of problem, where your SSH connection to an IoT device stops working remotely, is a common headache for many people, especially those just starting out with managing smart gadgets from a distance.
Many folks want to talk directly with their IoT devices using SSH. It is a way to get secure access and manage systems over a network that might not be safe. This method helps keep your important information private by encrypting data moving between devices and you. However, getting SSH to work with IoT devices over the internet can be a real challenge for many, so this post aims to make that process clearer, giving you some good steps to follow. You want to make sure your IoT device or embedded Linux system talks and takes orders without trouble, and that's what we'll help you with.
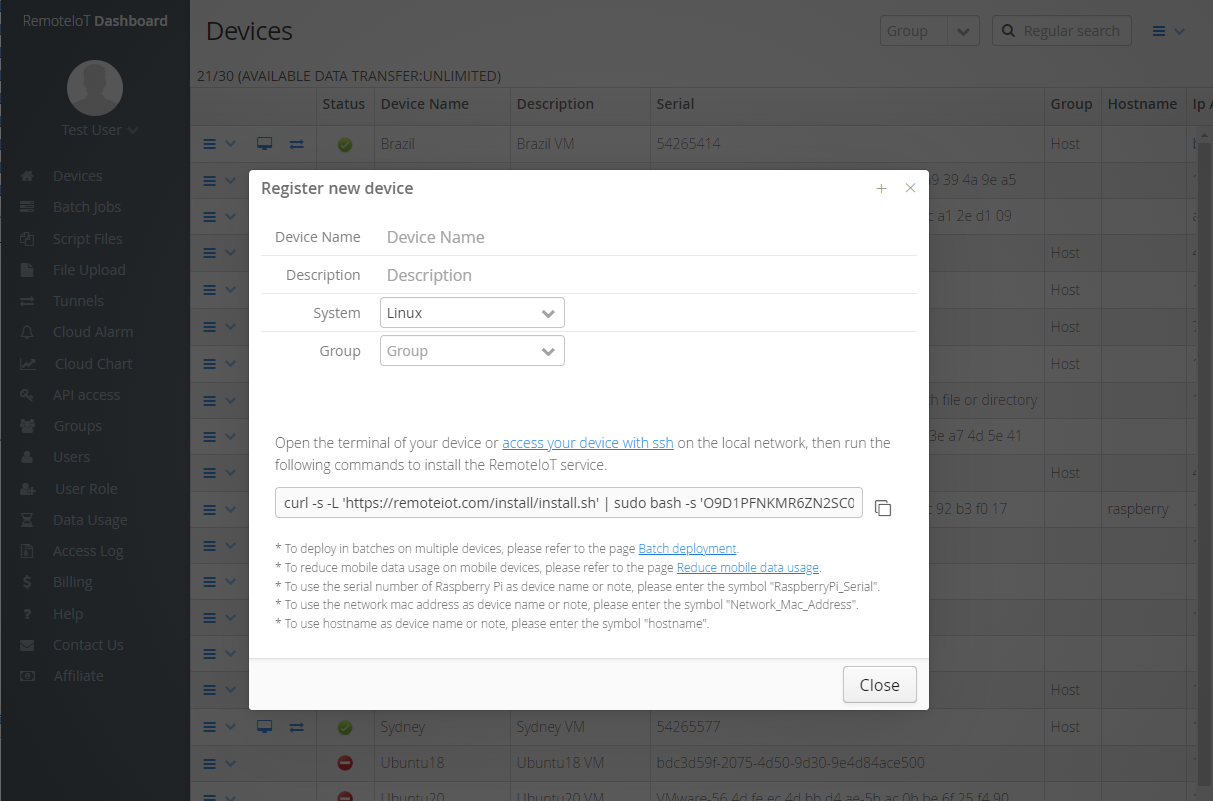
The idea of being good at remote SSH for your IoT devices, like a Raspberry Pi, means you can learn how to set it up, keep it safe, and fix common problems. It is, in a way, your free solution for keeping things running. With a correctly set up remote IoT platform and SSH on your Raspberry Pi, you can, quite literally, control it from anywhere in the world where you have an internet connection. So, if your remote IoT platform SSH key is not working on your Raspberry Pi, it truly locks you out. Let's figure out why that might be and how to get back in.
- Who Was Cameron Boyce Best Friend
- How To Apply Eyeliner
- Oil Before Or After Moisturizer Body
- Helices3d Twitter
- Acura Rdx
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Problem with SSH and IoT
- Common Reasons Your SSH IoT Device Isn't Connecting
- Step-by-Step Troubleshooting for SSH IoT Device Remotely Not Working
- Securing Your Remote IoT SSH Access
- When SSH Isn't Enough: Exploring Alternatives
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the Problem with SSH and IoT
Remote access is really important for handling servers, IoT devices, and even regular computers these days. SSH is one of the ways people often use for this. It gives you a safe way to get to your devices. Keeping IoT devices safe is a very big deal. SSH makes sure that data going between devices and users is kept secret, protecting important information. However, using SSH with IoT devices over the internet can bring some difficulties for many users. This blog tries to make that whole process clear, giving you a good path to follow.
Why SSH for IoT Can Be Tricky
Unlike a big server sitting in a data center, IoT devices often have limited power and memory. They might also be on networks that are hard to reach from the outside, like behind home routers or mobile hotspots. So, that can mean extra steps are needed to get SSH working. Also, you might be trying to connect to a Raspberry Pi, which is a very common IoT device, and sometimes the setup just doesn't go as planned. It's a bit like trying to talk to someone through a thick wall; you need to find a way for your voice to get through clearly.
Common Reasons Your SSH IoT Device Isn't Connecting
There are a few main reasons why your SSH connection to an IoT device might not be working from a distance. It usually comes down to something blocking the path, a setting on the device itself, or an issue with how you are trying to connect. We will look at these common points, so you can start figuring out what's going on. Knowing the typical culprits is the first step to getting things back in order, you know.
- Overbite Correction Before And After
- Roseanne Tom Arnold
- Ish Smith 2023 24 Hornets
- Hash Key
- Prince Ernst August Of Hanover
Network and Firewall Blocks
One of the most frequent reasons for connection problems is a block in the network. This could be a firewall on your home router, a firewall on the IoT device itself, or even your internet service provider (ISP) blocking certain kinds of traffic. For instance, if you're trying to reach your device from outside your local network, you need to make sure your router is set up to forward the SSH port to your IoT device. If it's not, the connection simply won't get through, and that's a pretty common issue.
SSH Service Issues on the Device
Sometimes, the problem isn't with the network, but with the SSH service on the IoT device itself. The SSH daemon (the program that listens for SSH connections) might not be running, or it could be set up incorrectly. It might have crashed, or maybe it wasn't even started after a reboot. You need to confirm that the SSH service is active and listening for incoming connections on the correct port. This is a very basic check, but it's often overlooked, you know.
SSH Key and Authentication Troubles
If you're using SSH keys for security, which is a good idea, issues with these keys can definitely stop you from connecting. Perhaps your remote IoT platform SSH key is not working on your Raspberry Pi. This could be because the key file on your client computer isn't in the right spot, has the wrong permissions, or maybe you are trying to use a key that doesn't match the one on the IoT device. You might need to connect to a SSH proxy server using a SSH keypair that you made just for it, not your usual `id_rsa` keypair. The `.ssh` directory is not always created by default under your home directory, so when you call `ssh somehost` (replacing 'somehost' with the name or IP of a host running sshd), the directory and keys need to be in place. The default key for an older protocol version, for example, is `~/.ssh/identity`.
Client-Side Configuration Hiccups
Even if the device and network are fine, your client program (like PuTTY or your terminal) might have a small error in its settings. This could be a wrong IP address, an incorrect port number, or issues with how it's trying to use your SSH key. You might also have problems if you are trying to forward X11 connections for a graphical user interface (GUI) and your display settings aren't right. If you run `ssh` and `DISPLAY` is not set, it often means SSH isn't forwarding the X11 connection. To confirm that SSH is forwarding X11, you can look for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in the output. It's a subtle thing, but very important for some uses.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting for SSH IoT Device Remotely Not Working
When your remote SSH connection to an IoT device isn't working, it's best to go through a checklist of possible problems. This helps you narrow down the issue and find a solution. We will go through each step carefully, so you can tackle the problem methodically. This way, you can get back to managing your devices, you know, without too much trouble.
Check Network Connectivity
First, make sure your IoT device is actually connected to the internet. Can it ping other websites? Can you ping the IoT device's local IP address from another device on the same network? If you can't even reach it locally, then the problem is likely with the device's Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection, not SSH itself. If it's connected locally, try to ping its public IP address from an outside network. If that fails, the issue is probably with your router's port forwarding or your ISP.
Verify SSH Service Status on the IoT Device
You need to confirm that the SSH service is running on your IoT device. If you can access the device locally (perhaps with a keyboard and screen, or another local access method), open a terminal and type `sudo systemctl status ssh` (for systems using systemd, like most modern Linux distributions). If it's not running, try starting it with `sudo systemctl start ssh`. If it's enabled to start on boot, you can check with `sudo systemctl is-enabled ssh`. If it's not, you might want to enable it using `sudo systemctl enable ssh` to make sure it comes up after a restart. This is a pretty basic step, but it's very important.
Look at Firewall Rules
Both on the IoT device and on your network router, firewalls can block SSH connections. On the IoT device, check if a firewall like `ufw` or `iptables` is blocking port 22 (the default SSH port). You might need to add a rule to allow incoming connections on that port. For example, with `ufw`, you would use `sudo ufw allow ssh` or `sudo ufw allow 22/tcp`. On your router, you need to set up "port forwarding" to direct incoming SSH traffic from the internet to your IoT device's local IP address. If you are trying to avoid port forwarding or firewall pinholing, you might need a different kind of remote access solution, which we will talk about a little later.
Inspect SSH Keys and Permissions
If you're using SSH keys, make sure your private key on your client computer has the correct permissions (usually `chmod 400` or `chmod 600`). The public key on the IoT device, located in `~/.ssh/authorized_keys`, also needs the right permissions (`chmod 600` for the file and `chmod 700` for the `.ssh` directory). If you created a specific keypair for a proxy server, you need to make sure you are telling your SSH client to use that particular key file. For example, when you run `ssh`, you can use the `-i` option followed by the path to your private key file, like `ssh -i /path/to/your/private_key user@your_iot_device`. This is a very common point of error, actually.
Custom SSH Port Settings
Some people change the default SSH port (22) to a different one for security reasons. If your IoT device's SSH service is listening on a non-standard port, say 5643, you need to specify that port when connecting from your client. You can do this with the `-p` option: `ssh -p 5643 user@your_iot_device`. My text mentions that after restarting the socket with `systemctl edit ssh.socket [socket] listenstream= listenstream=5643` and then `systemctl restart ssh.socket`, they were able to connect to SSH via the new port. This shows that changing the port on the server side requires the client to know about it too. It is a bit of a manual adjustment, you know.
X11 Forwarding and GUI Access
If your goal is to get a graphical interface over SSH, you need X11 forwarding to be set up correctly. On the client side, you might need an X server program (like Xming on Windows or XQuartz on macOS). On the SSH client command, you would typically use the `-X` option: `ssh -X user@your_iot_device`. If you run `ssh` and the `DISPLAY` environment variable is not set on the remote side, it means SSH is not forwarding the X11 connection. To confirm that SSH is trying to forward X11, you should check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in the output of your SSH client, perhaps by adding a `-v` for verbose output. This is very specific to needing a GUI, obviously.
MAC Algorithm Compatibility
Sometimes, older IoT devices or newer client software might have issues with the "Message Authentication Code" (MAC) algorithms they support. The list of supported MAC algorithms is set by the `MACs` option, both in `ssh_config` (client side) and `sshd_config` (server side). If this option isn't there, the default algorithms are used. If you want to change the values, you might need to edit these configuration files to include algorithms that both your client and server can agree on. This is a rather advanced troubleshooting step, but it can solve some stubborn connection issues, you know.
Securing Your Remote IoT SSH Access
Beyond just getting SSH to work, keeping your IoT devices safe is a top concern. Always use strong, unique passwords if you're not using keys. Better yet, switch to SSH key authentication and disable password login entirely. This makes it much harder for unwanted guests to get in. Also, keep your device's software updated, as updates often include security fixes. Regularly review who has access and what permissions their keys have. This is a very basic security practice, but it's very effective, you know. Learn more about IoT security on our site.
When SSH Isn't Enough: Exploring Alternatives
While SSH is great for direct, secure access to individual devices, it can become a bit much when you have many IoT devices. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) often find they outgrow SSH fast. The future of IoT management is moving toward systems that need very little human work but still perform at their best. For larger deployments, or when you need to manage devices without direct port forwarding, you might want to look at remote IoT device management solutions. These platforms can give you control over many devices from one spot, often without needing you to open ports on your router or deal with complex firewall rules. They offer a more scalable way to handle your IoT fleet. You might also consider other remote access methods for different needs; for example, some people ask about enabling RDP for Intune-managed devices, which is a different protocol for Windows systems. But for Linux-based IoT, specialized remote management solutions are often a better fit for big projects. You can also find out more about remote IoT management solutions here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people ask when their SSH to an IoT device isn't working:
How do I fix SSH connection refused on Raspberry Pi?
If you get "connection refused," it often means the SSH service isn't running on your Raspberry Pi or a firewall is blocking the connection. Check if the SSH daemon is active using `sudo systemctl status ssh` on the Pi itself. Also, make sure no firewall rules are stopping the
- Claire Black Letspostit
- Rollie Pollie Toy
- How Old Is Dana Perino Husband
- How Many Stanley Cups Does Sidney Crosby Have
- Bmw Of Bellevue Service Center
How to remotely ssh iot device in web browser
IoT SSH Remote Access - SocketXP Documentation

How Do I Access My IoT Device Remotely? | Robots.net