Unlock Your IoT Devices: Free SSH Connect Apps For Easy Access
Have you ever found yourself wondering how to get a better handle on your small, smart devices, the ones that make up your Internet of Things setup? It's a common thought, too, especially when you need to peek behind the curtain or perhaps make a quick adjustment. We're talking about those times you wish you could just 'talk' directly to your smart home gadgets, your tiny development boards, or even that local server humming away in the corner. Well, it's actually more straightforward than you might think, and it often involves a wonderful tool called SSH.
Connecting to these devices securely, without spending a dime on fancy software, is a real possibility. Many folks, myself included, have found that a free SSH connect app can be a true helper for managing everything from a small Raspberry Pi project to a local server running services like Elastix. It’s a way to send commands, transfer files, and generally keep tabs on your setup, all from the comfort of your computer or even your phone, which is pretty neat.
Sometimes, getting these connections just right can be a bit tricky, though. Perhaps you've had a moment where SSH wasn't quite working after a new software install, like when I put GitLab on my server, and suddenly, my usual SSH access seemed to hit a snag. Or maybe you've changed a password, like my Apple ID password, and then things felt a little off with your Mac's connections. These little bumps in the road are actually quite common, and understanding how free SSH connect apps work can help smooth them out, giving you reliable access to your IoT world.
- Pat Benatar Style
- Acadia Veneer
- Was Haley Really Pregnant In Season 4 Of One Tree Hill
- Johnathon Caine Age
- Frankie Katifias
Table of Contents
- What is SSH and Why It Matters for Your IoT?
- Why Choose a Free SSH Connect App?
- Common Ways to Use SSH for Your IoT Devices
- Picking a Good Free SSH Connect App
- Getting Your SSH Connection Ready
- Sorting Out Common SSH Connection Issues
- Keeping Your IoT Connections Safe and Sound
What is SSH and Why It Matters for Your IoT?
SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, is basically a way to connect to another computer over an unsecured network in a very safe manner. It's like having a secret, protected telephone line straight to your device. For your IoT gadgets, this means you can send commands, look at files, and do pretty much anything you'd do if you were sitting right in front of it, but from anywhere with an internet connection. It’s a bit like magic, really, and quite helpful for managing things remotely, which is why it's so popular for small servers and IoT projects.
So, why is this important for your IoT setup, you ask? Well, many IoT devices, like a Raspberry Pi or an Arduino with network capabilities, don't have a screen or keyboard attached. You can't just plug in a monitor and start typing. SSH gives you that text-based interface, a command line, to interact with them. It means you can update software, check sensor readings, or restart services without having to physically touch the device, which is pretty convenient, too it's almost.
It also offers strong security. When you use SSH, all the information exchanged between your computer and your IoT device is encrypted. This keeps your commands, passwords, and any data you're looking at private, away from prying eyes. This secure tunnel is a big deal, especially when your devices are connected to the internet, because you want to keep them protected from unwanted access, you know.
- Is Karen Fukuhara Single
- Does Harrison Ford Really Have Parkinsons
- Nicolenurko Erome
- Sleep Sack Guide
- Who Voiced Officer Tenpenny
Why Choose a Free SSH Connect App?
Choosing a free SSH connect app just makes sense for many people, especially when you're just getting started with IoT or managing a home lab. There's no need to shell out money for something that powerful, reliable tools can do without any cost. These free options often provide all the features you'd typically need for day-to-day management of your IoT devices, from basic connections to more advanced tasks like file transfers and port forwarding. It's a bit like getting a really good tool for free, which is always a nice bonus.
The accessibility of free apps is another big plus. You can usually download them quickly and get them running on various operating systems, whether you're using Windows, macOS, or Linux. This means you're not tied to a specific platform or forced to buy new software just to get connected. Many of these free tools are also open source, which means a large community of developers and users often supports them, leading to regular updates and improvements, which is rather reassuring.
For personal projects, learning, or even small-scale deployments, free SSH apps offer incredible value. They let you experiment, troubleshoot, and manage your devices without any financial barrier. This freedom to explore and build without worrying about software costs can really encourage innovation and learning in the IoT space, which is something we all appreciate, actually.
Common Ways to Use SSH for Your IoT Devices
SSH is incredibly versatile for managing IoT devices, and there are many practical situations where a free SSH connect app really shines. From keeping an eye on your local server to sorting out tricky network issues, it's a tool that comes in handy quite often. We can look at a few common scenarios where it proves its worth, you know, based on real-world experiences.
Managing Local IoT and Servers
One of the most frequent uses for SSH is to manage devices that are on your local network. Think about that small server you might have running, perhaps for home automation or even something like Elastix, which is a communication server. Being able to connect to it via SSH means you can install updates, change settings, or check its status without needing a monitor or keyboard directly attached. It's like having a remote control for your server, which is super convenient, really.
For instance, I use my server locally for various services, and being able to SSH into it from my main computer makes maintenance a breeze. It’s always connected and works properly when I'm in my workspace, giving me that direct line to make sure everything is running smoothly. This kind of access is pretty fundamental for anyone with a home lab or a collection of smart devices, as a matter of fact.
Fixing Connectivity Troubles
Sometimes, things just don't go as planned with network connections, and SSH can be your first stop for troubleshooting. I've personally run into situations where, after installing new software like GitLab, my SSH connections suddenly stopped working correctly. Before that install, SSH was fine, so you know something changed. Using a free SSH app lets you get in there and figure out what went wrong, which is very helpful.
It's also useful for diagnosing issues related to how your client remembers host keys. You see, when you connect via SSH, every host has a key, and your client remembers the host key associated with a particular server. If that key changes, or if there's a mismatch, your connection might get blocked, which is a security feature. SSH gives you the messages you need to understand why it's not connecting, like the "you are connecting via the ssh protocol" message, and then you can take steps to fix it, which is pretty neat.
Securely Reaching Your Data
SSH isn't just for sending commands; it's also excellent for creating secure tunnels for other services. Imagine you have a database, like PostgreSQL 9.3, running on an Ubuntu server, and you want to connect to it from a different computer using a tool like pgAdmin III. Directly connecting to a database over the internet isn't always the safest choice, but SSH can create a secure pathway for that connection. So, if I SSH into the server via terminal, I'm able to connect with psql, but when I try to configure pgAdmin III to do the remote connection, it might struggle without an SSH tunnel. This tunnel keeps your database traffic safe, which is quite important.
This capability is a bit like having a private, encrypted pipe for your data, ensuring that sensitive information, like database queries or login details, stays protected as it travels across the network. It's a really good way to add an extra layer of security to applications that might not have strong encryption built in themselves, you know, like your database tools.
Seeing Your IoT with a Graphical Touch
For some IoT devices, or even a server, you might want a graphical interface rather than just a command line. This is where SSH's X11 forwarding comes in. If you run SSH and the display isn't set, it means SSH isn't forwarding the X11 connection, which is what allows graphical applications to show up on your local screen. To confirm that SSH is forwarding X11, you can check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in the output, which is a good tip.
I've thought about how to configure my Ubuntu 16.04 LTS server to have GUI access over SSH as an option, because sometimes a visual interface is just easier to work with. It's a way to reach your server from your workstation and see things graphically, which can be really helpful for certain tasks or for people who prefer a visual approach to system management, too it's almost.
Automating Tasks with Scripts
For those who like to automate things, SSH is a core component. You can write scripts, perhaps in Python or Bash, that connect to your IoT devices and execute commands automatically. I'm writing a script to automate some command line commands in Python, and at the moment, I'm doing calls like "cmd = "some unix command"". This means your script can log in, run a series of commands, and then log out, all without you having to type anything manually. It's a huge time-saver for repetitive tasks, basically.
For example, if you need to deploy updates to multiple IoT devices, a script can SSH into each one and run the update commands. Or if you need to pull data from various sensors at specific times, a script can handle that. This level of automation is incredibly powerful for managing a fleet of IoT devices efficiently, and it's something free SSH connect apps fully support, you know.
Picking a Good Free SSH Connect App
When you're looking for a free SSH connect app, there are a few things to keep in mind to make sure you pick one that works well for you. The "best" app often depends on your operating system and what you plan to do with it. For Windows users, PuTTY is a very popular choice, and many are accustomed to using it or an OSX command line terminal to SSH into a NAS, without any configuration of the client. It's simple, reliable, and gets the job done for basic connections, which is pretty handy.
For macOS and Linux, the built-in terminal usually has SSH capabilities already, so you might not even need to download an extra app. You just open your terminal and type "ssh somehost" (replacing 'somehost' with the name or IP of your device). This makes it very convenient, as you're using tools that are already part of your system. Many free options also offer features like managing multiple connections, saving login details, and supporting different types of authentication, which can be a real time-saver, actually.
Look for apps that are regularly updated and have a good community backing. This suggests that any little problems will likely get fixed quickly and that the app will stay compatible with newer operating systems and security standards. A good user interface, if you prefer one, can also make a big difference in how easy it is to use, which is something to consider, too it's almost.
Getting Your SSH Connection Ready
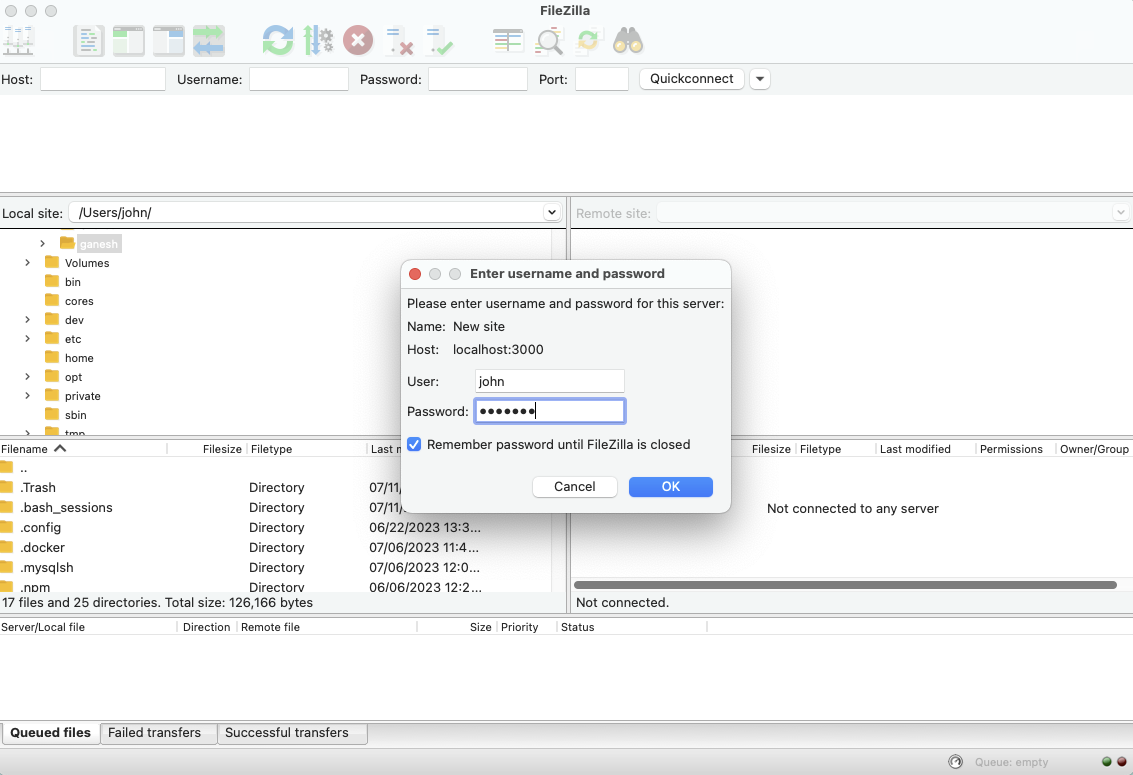
Before you can connect to your IoT device with a free SSH app, you need to make sure a few things are set up correctly. The most important part is usually the SSH keypair. This is like having a lock and a key: the public key goes on your IoT device, and you keep the private key safe on your computer. When you try to connect, your computer uses its private key to prove who it is to the device, which is a very secure way to log in without needing to type a password every time, you know.
Often, your default keypair is located in a hidden folder called `.ssh` within your home directory, like `~/.ssh/identity` for older protocol versions. However, the `.ssh` directory is not by default created below your home directory; it gets made when you first use SSH, like when you call `ssh somehost`. If you need to connect to an SSH proxy server using a specific SSH keypair that you created just for it (not your default `id_rsa` keypair), you'll need to tell your SSH client which private key to use, which is a bit more advanced but totally doable. This usually involves specifying the key file in your command or setting it up in your SSH configuration file, which is called `config` inside your `.ssh` folder, which is quite flexible.
Sometimes, you might also need to adjust the port your SSH server listens on. The standard SSH port is 22, but for security or to avoid conflicts, some people change it. For instance, after restarting the socket, we were able to connect to SSH via the new port after running `systemctl edit ssh.socket` and setting `ListenStream=5643`. Knowing how to change this, both on the server and in your SSH client, is a useful bit of knowledge, which is rather practical.
Sorting Out Common SSH Connection Issues
Even with free SSH connect apps, you might run into a few bumps along the way. It's totally normal, and many of these issues have straightforward solutions. I've had my share of connection woes, from Git issues to Mac problems, and figuring them out often comes down to checking a few key things, you know.
Checking Your Keys and Permissions
One very common reason SSH connections fail is due to problems with your SSH keys or their permissions. After installing Git on my new work computer, generating my SSH key, and adding it on GitLab, I was trying to clone a project but kept getting an error. This often means the key isn't set up right on the server, or the permissions on your private key file on your computer are too open. SSH is very picky about private key file permissions; they need to be very strict to keep them safe, which is a good thing, really.
If you're trying to SSH to server 2 using your private key file from server 1, you need to make sure that key is accessible and that the permissions are correct. Sometimes, a simple command can fix permissions, like the one I took from Git's documentation to resolve an issue for each repo. It's usually a quick fix once you know what to look for, which is pretty reassuring.
Dealing with Host Key Warnings
Remember how clients remember the host key associated with a particular server? If that host key changes, or if you're connecting to a new server for the first time, you might get a warning message. This is SSH's way of telling you, "Hey, this server's identity seems different, are you sure you want to connect?" It's a security measure to prevent something called a "man-in-the-middle" attack. You'll typically be asked to confirm if you want to accept the new key, and if you know the change is legitimate (like a server reinstallation), then it's usually fine to accept it, you know.
If you're constantly getting host key warnings for the same device, it might mean there's something amiss, or perhaps you have multiple entries for the same IP address in your `known_hosts` file. Clearing out the old entry for that specific host usually sorts it out, which is a fairly common troubleshooting step.
Port Mix-Ups
Sometimes, your SSH server might not be listening on the standard port 22. This could be for security reasons or because another service is using that port. If you try to connect to the wrong port, your connection will simply fail. I've seen situations where after restarting the socket, we were able to connect to SSH via a new port, like 5643, because the server was configured to listen there. So, if you're having trouble connecting, it's always worth checking if the SSH server on your IoT device is using a non-standard port, and then specifying that port in your SSH command, which is a pretty simple fix.
This is a bit like trying to call someone but dialing the wrong number; you just won't get through. Making sure your SSH client and the SSH server on your IoT device are both set to use the same port is a fundamental step for a successful connection, which is actually quite important.
X11 Forwarding Hiccups
If you're trying to get a graphical interface over SSH and it's not working, it's often an X11 forwarding issue. As mentioned, if you run SSH and display is not set, it means X11 forwarding isn't happening. To confirm it's forwarding, you'd look for "requesting X11 forwarding" in the output. If it's not there, you might need to enable it on both your client (using the `-X` or `-Y` option with your SSH command) and on the server side in the `sshd_config` file. Sometimes, the necessary X11 packages might not even be installed on your IoT device, which would also prevent it from working. So, installing those and configuring the server is a good place to start, you know.
This can be a bit more involved than a simple connection, but for those times you really need a GUI, it's worth the effort. It's about making sure all the pieces are in place for the graphical information to travel across your secure SSH tunnel, which is quite a neat feature.
Apple ID and Keychain Challenges
For Mac users, sometimes system-level changes can affect SSH. I met this issue after I changed my Apple ID password, so I updated my Apple ID and restarted my Mac, and then some SSH connections felt off. This can happen because your Mac's keychain might store SSH key passphrases, and a password change can sometimes cause a hiccup. Often, simply restarting your Mac or re-adding your SSH key to your SSH agent can resolve these kinds of issues, which is a simple thing to try, basically.
It's a reminder that your operating system's settings and how it manages credentials can play a part in your SSH experience. Keeping your system updated and being aware of how it interacts with your SSH keys can save you some head-scratching moments, which is a good habit to get into, you know.
Keeping Your IoT Connections Safe and Sound
Once you've got your free SSH connect app working smoothly with your IoT devices, it's really important to think about keeping those connections secure. SSH is designed to be secure, but there are always steps you can take to make it even safer. One big thing is to always use SSH keypairs for authentication instead of passwords. Passwords can be guessed or brute-forced, but SSH keys are much harder to compromise, which is a significant improvement in security.
Also, consider changing the default SSH port (usually 22) on your IoT devices to a different, non-standard port. While this doesn't stop a determined attacker, it does make your device less visible to automated scanning tools that only look for the default port. It's a bit like moving your front door to a less obvious spot, which can deter casual intruders, you know. For example, after restarting the socket, we were able to connect to SSH via the new port, which shows how simple it is to change.
Regularly update the software on your IoT devices and your SSH client. Updates often include security patches that fix known weaknesses, keeping your connections protected from the latest threats. You should also be careful about which MAC algorithms are supported. The list of supported MAC algorithms is determined by the `macs` option, both in `ssh_config` and in `sshd_config`. If it's absent, the default is used. If you want to change the value, it's a setting you can adjust for better security, which is quite a good thing to be aware of.
Finally, always be cautious about connecting to unknown Wi-Fi networks when managing your IoT devices. Public Wi-Fi can be risky. If you must connect from an unsecured network, consider using a VPN as an extra layer of protection over your SSH connection. This adds another shield to your data, which is always a good idea when dealing with sensitive access, you know. Learn more about secure remote access on our site, and link to this page https://www.example.com/iot-security-tips.
- What Is Chris Pratts Net Worth
- Sophie Cunningham
- Did Benedict Cumberbatch Play Dr Who
- Daaku Twitter
- Yoo Jungkook

IoT Connect APK Download for Android - Latest Version
IoT SSH Remote Access - SocketXP Documentation
IoT-powered app - Our Portfolio - Aimprosoft